Source Destination Cut
As an important editing function in Sequoia, source-destination cutting is particularly suitable for classical music productions, for montage work, and for current productions, whereby editing operations can be performed while a recording is still in progress.
The source-destination cutting method effectively and intuitively combines the advantages of a linear audio editing suite, consisting of a player and recording device, with those of a non-linear editor. In a special source-destination cut mode, two screen areas allow simultaneous and independent display and playback of the source tracks and the destination tracks. The lower monitor area (Source) displays the source material, i.e. all of the tracks recorded (including all of its takes).
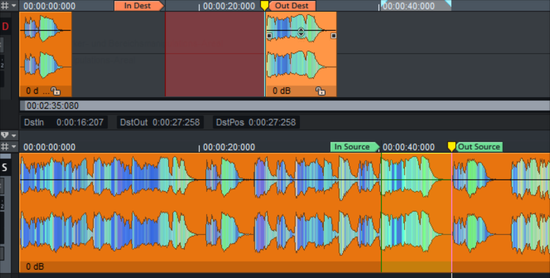
The upper area contains the target tracks (Destination). Here the edited material can be arranged using the mouse or the keyboard. You can move independently in both areas, scroll the section, zoom and play. You can move through the source while the destination is being played back to prepare for the next cut.
The actual editing takes place via markers. In and out markers in the source are used to define the material that is to be copied to a marker position in the destination by the cut command.
This function can be used to quickly perform editing processes that would otherwise be very time-consuming. For example, you can use 4-point editing to replace a section of your multitrack project with a slower version of the arrangement. With this process the subsequent audio material is moved on the new cut borders synchronously over all tracks.
You can use the source-destination cut features in any multitrack project. There are also additional modes available, i.e. S/D Special Mode and Multi-Source Session and the Multi-Synchronous Cut.
In this chapter