Objects
The audio data is represented in Sequoia projects by objects in the tracks. Objects are playable and editable entities in the project window of Sequoia, which can be moved, copied or cut on the tracks as desired.
An object is an representation of an audio file or part of it and contains references to the underlying audio files, which are visualized in a waveform display. An audio object accesses audio data and adds a variety of object-specific settings in real time: Volume, pan, object length, sound changes, fades, pitch changes, time stretching, AUX send taps, and effects. All these settings are only added to the original material afterwards, which itself remains untouched on the hard disk (non-destructive editing).
MIDI data is also represented by objects. MIDI objects contain playback instructions for MIDI devices or VST instruments in MIDI format. Unlike audio objects, MIDI data is stored together with the objects and is directly linked to the respective objects. For MIDI objects, read the chapter MIDI!
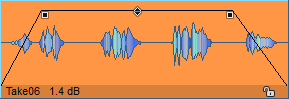
There are various handles on the objects that can be used to directly change the most important object properties: start time, length, fade-in and fade-out, and object volume. Other object properties, such as panorama
Objects that overlap in a track can be blended into each other. For more precise setting of such a crossfade there is a Crossfade Editor.
With the lock icon at the bottom you can lock an object and thus protect it against accidental changes.
The visual appearance of the objects can be configured very flexibly. You can access the display options via the menu View > VIP display > Project display... or with the keyboard shortcut Shift + Tab. For detailed information on the project display options, see the section in the System options >Project display.
In this chapter