Snap
The snap makes it easier to work with the mouse when moving objects and selecting ranges by snapping the moved markers or objects to specific positions, so you don't have to position the mouse exactly and still get exact positions. Beat divisions, markers, object edges, frames or the set quantization value can serve as snap positions.
Snapping means that if a marker, an range border or an object is moved close enough to a possible snap-in position, it automatically jumps to exactly this position, it “snaps” into this position.
"Close enough" refers to the screen display, i.e. the distance of the object from the desired position in screen pixels. If you have zoomed in to just a few bars, but have the snap set rather coarse (e.g. 1/2 notes), it is possible that objects can be moved to positions between snap positions.
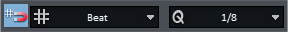
Using the Snap and Quantize menu on the top toolbar, you can define the most important snap settings and turn the snap on and off.
The complete snap and grid settings can be reached via the dialog Project options - General (keyboard shortcut I).
|
To turn the snap on and off, click the button with the magnet or select Menu View > Grid > Snap Active (keyboard shortcut: Ctrl + '). |
|
In the snap menu next to it you can select the type of the snap:
-
Snap to objects: With snap to objects the range selection, the play cursor and other markers snap to the edges of all objects in the project when they are moved. In addition, either object start or object end snap to all markers and to the edges of the other objects when moving objects. Whether the start or end position of the object snaps depends on whether the object is clicked in the front or rear half to move it. The shape of the mouse pointer indicates which edge is being snapped to:
-
 snaps to the left edge of the object
snaps to the left edge of the object -
 snaps to the right edge of the object
snaps to the right edge of the object
-
-
Snap to beats/bars: This option activates a snap grid that uses beat subdivisions as a basis. The beat snap ensures that when selecting ranges and moving objects and object edges, the play cursor and other markers, the time positions "snap" to defined values determined by the snap width. So, for example, if you have set a beat snap with a one bar snap width, you can click on the grid bar only approximately near the beginning of a bar to place the play cursor exactly at the beginning of the bar.
The beat snap also determines the step size when moving play cursor and range boundaries with the keyboard (arrow keys and shift + arrow keys).
If you have set a very coarse snap width (e.g. 2 bars), but zoomed in strongly, it may seem as if objects cannot be moved at all, because possible snap positions are very far away from the starting position on the screen or outside the visible section.
-
Snap to beats/bars (relative): This option also activates a snap grid that uses beat subdivisions as a basis. Relative means that for example the position of an object can only be changed stepwise in the set snap width, as with the normal beat snap, but the distance to the respective snap position remains the same. It therefore does not snaps on the beats, but in each case at the same distance before or behind them.
-
Snap to frames: This sets the snap width to the length of one SMPTE frame, according to the project frame rate set at Project Settings > Synchronization. This setting is important for video dubbing, the time positions then correspond exactly to the frames in video files.
-
Frame raster (relative): As with the relative beat snap, the frame snap here preserves the relative distance to the respective snap point.
-
With Snap to range the grid is similar to the beat grid, except that the snap width is defined by selecting a range before activating the grid. The length of this range then corresponds to one bar, and the snap width can be divided according to the Q value as with the beat snap.
In the lower part of the menu there is a selection of settings for the snap width for the beat snap:
-
Snap to quantization: Select the snap width in the Quantization menu (see below) and activate this setting to use this value also for the beat snap.
-
Every 4 bars, 2 bars, Full bar: To keep the menu manageable, all smaller values for the snap width are missing here. Set the values in the quantization menu and select Snap to quantization. Only the very large values for the snap width (which are also not useful as quantization values) can be set directly in the menu. If you absolutely want to set a value other than the quantization value for the snap width, you can do so in the Project Options under Snap/Grid. To do this, go to the menu File > Project properties > Project options….
-
Beat: The denominator of the time signature is used as the snap value, i.e. ¼ in 4/4 time and ⅛ in 3/8 time. The snap thus follows the time signature and takes time signature changes into account.
In the Quantization menu you set the quantization value Q, which is used for the audio- and MIDI-quantization and also serves as a setting for the snap width in the snap setting Snap to quantization. By default, the Q values of audio and MIDI quantization are linked to each other. Right-clicking on the field opens the MIDI quantization settings.
